Understanding the Different Types of Market Trading Days: A Guide for Traders
As a new trader entering the world of day trading, it's essential to understand that not all market days are the same. Each trading day presents unique characteristics and patterns that can significantly impact your trading strategy and outcomes. This is particularly important if you trade index products like SPY, SPX, ES, QQQ, NQ, etc. By recognizing and adapting to these different types of market trading days, you can enhance your decision-making abilities and increase your chances of success. In this article, we will explore the six main types of market trading days and discuss their key features, providing valuable insights for newer traders. If you are unfamiliar with the trading strategies that are listed below, sign up for the Options Mastery Course (OMC). The OMC details the setups and strategies that we use on a daily basis in the Trader’s Thinktank to extract profit from the market.
A goal that every trader has is to identify what type of trading day it is as early as possible into the trading session. Having this knowledge is incredibly advantageous to the active trader. One of the best ways to do this is to use Multiple Timeframe Analysis. It is also beneficial to be in the Trader’s Thinktank, as we provide a market outlook in our Premarket Prep notes that highlights what the expectations for the trading day are.
Trend Day
A trend day occurs when a particular direction dominates the market throughout the entire trading session. It is characterized by strong, sustained price movements in a single direction, either bullish or bearish. In a bullish trend day, prices consistently make higher highs and higher lows, while a bearish trend day exhibits lower highs and lower lows.
Key features:
Price moves in a clear and continuous direction
Volume tends to be higher than average
Indicators such as VWAP show strong alignment
Pullbacks are shallow and limited, making it challenging to enter counter-trend trades
Trading strategies:
Look for pullbacks to join the prevailing trend
Implement trend-following strategies
Place stop-loss orders at the nearest structure to protect against sudden reversals
Do not fade trend days
Double Distribution Trend Day
A double distribution trend day is an extension of a regular trend day. It exhibits two distinct price distribution phases within the trading session, with each phase characterized by a different price range. The first distribution typically follows the morning market open, while the second occurs later in the day.
Key features:
The market opens with a strong trend, followed by a brief consolidation phase
After the consolidation, a new trend emerges, usually with higher volatility
Volume tends to increase during the second distribution phase
Traders may observe volume patterns indicating exhaustion near the end of the day
Trading strategies:
Take advantage of the consolidation phase to identify potential breakouts
Use volatility indicators to adjust position sizing and risk management
Monitor volume patterns for signs of trend continuation or exhaustion
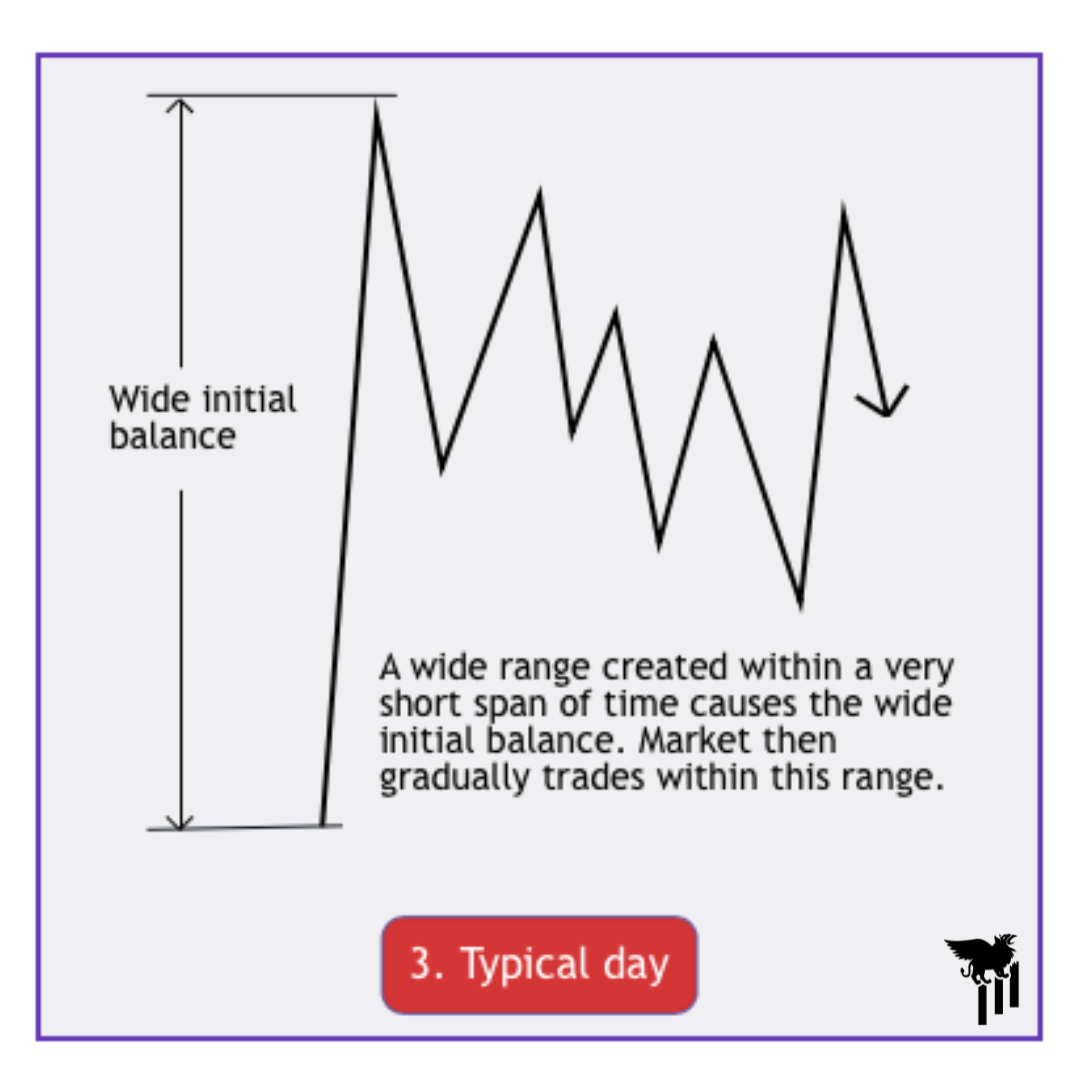
Typical Day
A typical day is characterized by a balanced (range-bound) market, where buying and selling pressures are relatively equal. The price action oscillates within a defined range, often forming recognizable chart patterns. This type of market day may lack a clear trend and can be challenging for inexperienced traders. Many new traders will lose money on a typical day, especially if it follows a trend day. One of the main benefits in the Trader’s Thinktank are the daily Premarket Prep notes, where we detail the market outlook for the day. This helps traders avoid choppiness.
Key features:
Price moves within a defined range without a strong directional bias
Volume and volatility may be moderate compared to trend days
The market often tests both support and resistance levels
Well-known consolidation patterns may form, but likely won’t offer strong opportunities
Generally want to avoid trading on these days depending on the available risk:reward setup
Trading strategies:
Identify and trade range-bound opportunities using support and resistance levels
Look for breakouts or breakdowns from consolidation patterns with tight targets and stops
Implement mean-reversion strategies by buying near support and selling near resistance
Remain in cash and wait for better opportunities
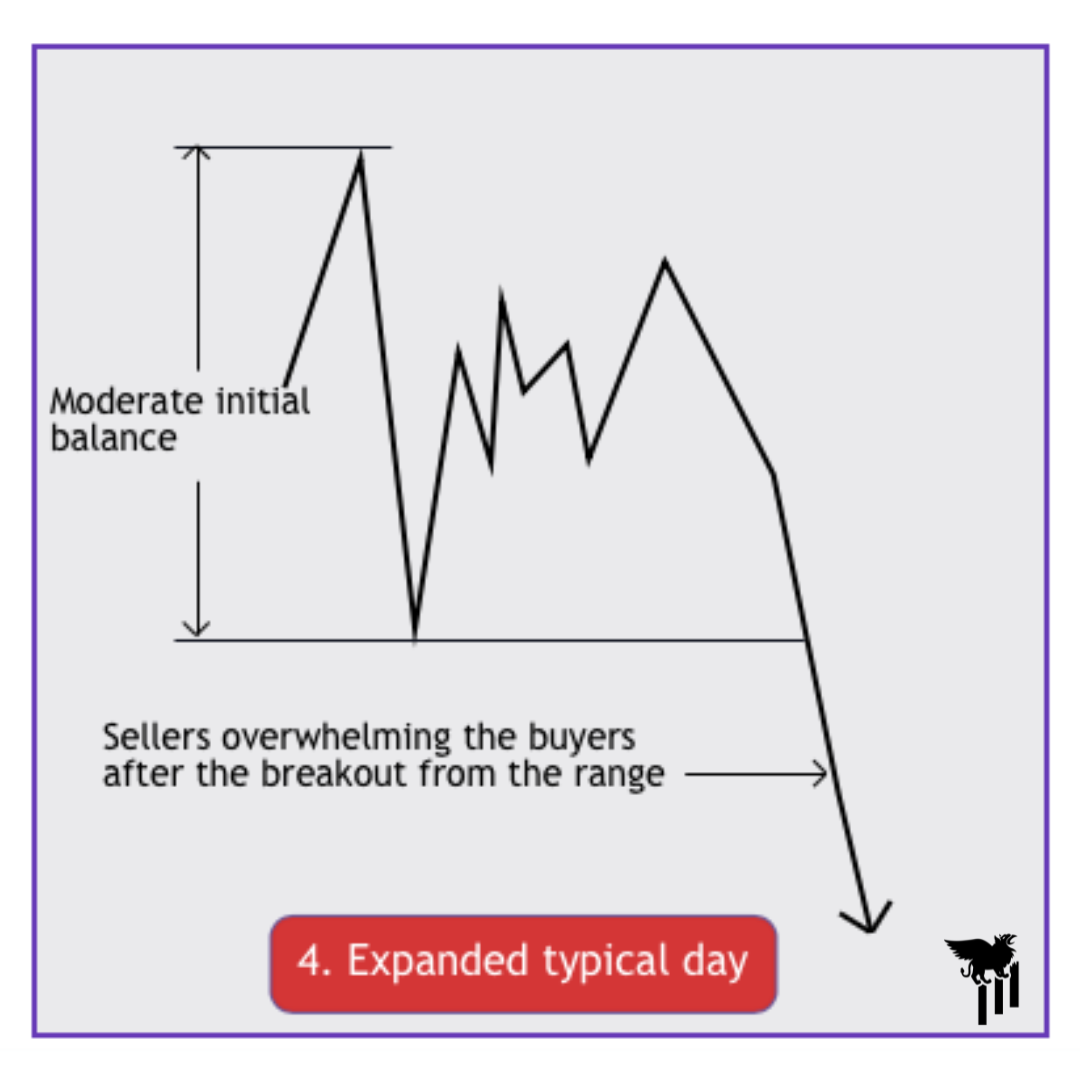
Expanded Typical Day
An expanded typical day is an amplified version of a typical day, characterized by increased volatility and larger price ranges. It usually occurs in response to significant news events, economic data releases, or unexpected market developments.
Key features:
The market experiences wider price swings compared to a regular typical day
Volume tends to be higher due to increased market participation
News releases or market shocks may trigger large price movements
Trading strategies:
Adapt your risk management approach to account for increased volatility
Be cautious with entering trades immediately after news releases or market shocks
Look to utilize mean-reversion strategies near the edge of the day’s range
Trading Range Day
A trading range day occurs when the market exhibits a narrow price range, often staying within defined support and resistance levels. It is characterized by price oscillations between these boundaries, lacking a strong trend or directional bias. These are usually great days for an active intraday trader.
Key features:
Price moves sideways, frequently testing support and resistance levels
Volume and volatility are typically lower than average
Traders may observe the formation of range-bound patterns
Breakouts from the range may lead to trend days or provide trading opportunities
Trading strategies:
Trade range-bound opportunities by buying near support and selling near resistance (double check risk:reward)
Monitor price action and volume for signs of a breakout or breakdown
Adjust position sizing and risk management due to lower volatility
Sideways/Choppy Day
A sideways or choppy day is characterized by erratic price movements with no clear direction or sustained trend. The market lacks conviction, and price action appears random, making it challenging to establish profitable trades. Beginner and developing traders usually fail to recognize the choppy day early in the session and end up losing money on these days.
Key features:
Price moves with no discernible trend, resulting in frequent reversals
Volume and volatility may be low, indicating reduced market participation
Technical indicators may provide conflicting or unreliable signals
Traders may experience multiple false breakouts or breakdowns
Trading strategies:
Exercise caution and avoid taking aggressive positions
Focus on short-term trades or scalping opportunities
Remain in cash
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of market trading days is crucial for traders, especially those new to the world of day trading. By recognizing the unique characteristics of trend days, double distribution trend days, typical days, expanded typical days, trading range days, and sideways/choppy days, you can adjust your trading strategies and decision-making accordingly. As mentioned previously, the goal is to establish what type of trading day it is as early as possible in the trading session. The easiest way to do this will be to lean on the experience of more seasoned traders by joining the team in the Trader’s Thinktank. Remember, no two trading days are exactly alike, and the ability to adapt to different market conditions is an essential skill for success in day trading. Continuously observing and analyzing market dynamics will enable you to refine your strategies and navigate the markets with confidence and agility.